Software development has undergone a dramatic transformation over the last two decades. Traditional methods that separated development and operations teams often led to delays, miscommunication, and inefficiencies.
Developers would write code, pass it to operations, and wait while deployment or maintenance slowed down the process. This disconnect not only impacted productivity but also affected customer satisfaction as businesses struggled to release updates quickly.
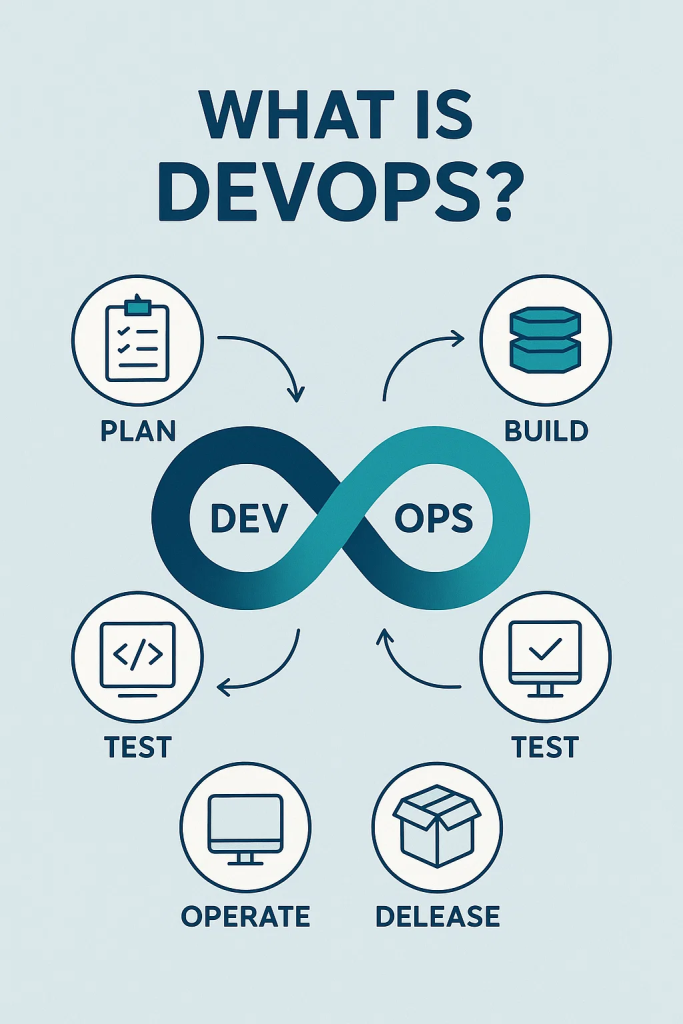
DevOps emerged as a solution to bridge these gaps by combining cultural philosophies, practices, and tools to improve collaboration, efficiency, and product quality. It brings development and operations teams together under a shared responsibility model while embracing automation to deliver faster and more reliable software.
In this article, we will explore what DevOps is, why it matters, and how it shapes the future of software delivery in today’s fast-paced digital economy.
The Evolution of DevOps: From Agile to Automation
DevOps did not appear overnight. It evolved as an extension of Agile practices, which emphasised flexibility, iterative development, and collaboration. While Agile improved development cycles, operational bottlenecks continued to be a challenge.
DevOps extended these ideas by fostering closer communication between developers and operations teams while embracing automation for testing, deployment, and monitoring. This shift not only accelerated software delivery but also fostered a cultural movement of shared responsibility across teams.
The following are the major milestones in the evolution of DevOps:
- Agile methodology encourages iterative releases
- The rise of cloud computing is enabling faster deployments
- Automation tools are reducing manual interventions
- Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines
- DevOps as a cultural movement beyond tools
Core Principles of DevOps
At its foundation, DevOps is guided by principles that emphasise collaboration, feedback, and automation. These principles are not limited to technical practices but extend into organisational culture.
By breaking down silos between teams, DevOps encourages shared goals and accountability. This results in shorter development cycles, quicker responses to customer needs, and better-quality software.
The following are the core principles that define DevOps:
- Collaboration: Encouraging open communication between development and operations
- Automation: Reducing manual errors and speeding up delivery
- Continuous Improvement: Iterating based on feedback loops
- Measurement: Tracking metrics to ensure progress
- Customer-Centric Mindset: Prioritising end-user satisfaction
Read about – The Advantages of Hybrid Cloud Computing.

Key Practices That Define DevOps
Beyond its principles, DevOps is implemented through specific practices. These practices operationalise the philosophy, making it tangible for teams. They are often interconnected, creating a feedback-driven system that accelerates innovation and reduces downtime.
By applying these practices consistently, organisations can build robust pipelines that ensure efficiency and resilience.
The following are the key practices of DevOps in action:
- Continuous Integration (CI): Developers merge code frequently to avoid conflicts
- Continuous Delivery (CD): Automating release cycles for faster delivery
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Managing infrastructure using code instead of manual setup
- Monitoring and Logging: Ensuring systems are healthy and reliable
- Automated Testing: Catching issues early to improve quality
DevOps Tools and Technologies Developers Rely On
DevOps is powered by a rich ecosystem of tools designed to automate processes and foster collaboration. These tools support various stages of the software lifecycle, from coding and testing to deployment and monitoring. Choosing the right combination depends on organisational needs, but some tools have become industry standards due to their reliability and scalability.
The following are popular DevOps tools across categories:
- Version Control: Git, GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket
- CI/CD Tools: Jenkins, CircleCI, GitHub Actions
- Configuration Management: Ansible, Puppet, Chef
- Containerisation: Docker, Kubernetes
- Monitoring Tools: Prometheus, Grafana, ELK Stack
Discover information on – How to Learn Cloud Computing.
Benefits of Adopting DevOps in Organisations
The adoption of DevOps goes far beyond technical improvements. It drives cultural change that enables teams to innovate more quickly and respond effectively to market needs. For businesses, DevOps represents not just an IT strategy but a competitive advantage.
By unifying teams and processes, companies experience reduced downtime, higher customer satisfaction, and more predictable outcomes.
The following are the main benefits of DevOps adoption:
- Faster software releases with reduced cycle times
- Improved collaboration between cross-functional teams
- Greater automation, reducing errors and manual work
- Enhanced system stability and reliability
- Continuous feedback leads to better customer satisfaction
Challenges in Implementing DevOps
While DevOps offers many advantages, its implementation is not without challenges. Organisations often underestimate the cultural changes required, focusing solely on tools and technology. Resistance from teams accustomed to traditional methods can also slow adoption.
Moreover, scaling DevOps across large enterprises requires consistent governance and standardisation. Recognising these challenges early helps businesses plan smoother transitions.
The following are the common challenges in adopting DevOps:
- Cultural resistance to collaboration
- Over-reliance on tools without a mindset shift
- Lack of skilled professionals
- Integration issues with legacy systems
- Maintaining security while accelerating delivery
Check out – Cloud Computing vs Artificial Intelligence.
DevOps vs Traditional IT Approaches
DevOps represents a significant departure from traditional IT management. In conventional setups, development and operations functioned in silos, often leading to delays and conflicts. DevOps eliminates this divide through automation and shared responsibility. Comparing the two approaches highlights why organisations are increasingly favouring DevOps for digital transformation initiatives.
Comparison Table: DevOps vs Traditional IT
|
Aspect |
Traditional IT |
DevOps |
|
Team Structure |
Separate development and operations teams |
Integrated cross-functional teams |
|
Deployment Frequency |
Infrequent, manual releases |
Frequent, automated releases |
|
Collaboration |
Limited communication, siloed processes |
Open communication and shared responsibility |
|
Automation |
Minimal automation, manual interventions |
High automation across CI/CD pipelines |
|
Feedback Loops |
Slow, delayed by silos |
Rapid, continuous feedback cycles |
Future of DevOps in AI and Cloud Environments
As organisations embrace cloud-native technologies and artificial intelligence, DevOps continues to evolve. AI-driven DevOps, often called AIOps, is gaining traction by using machine learning to predict system issues before they occur.
Cloud platforms further enhance DevOps capabilities with scalable infrastructure and integrated services. The future will likely see deeper convergence between AI, cloud, and DevOps, resulting in intelligent, self-healing systems.
The following are the trends shaping the future of DevOps:
- AI-powered predictive analytics for monitoring
- Greater use of serverless and cloud-native technologies
- Automated security integration (DevSecOps)
- Enhanced scalability with hybrid cloud adoption
- Increasing demand for AI and automation skills
Conclusion
DevOps is more than a methodology; it is a cultural and technical movement transforming how software is built, tested, and delivered. By uniting development and operations, organisations gain agility, reliability, and faster innovation cycles.
At Digital Regenesys, the Cloud Computing and DevOps Certificate Course complements DevOps knowledge by equipping professionals with AI-driven insights that can be applied to automation, monitoring, and decision-making.
Take the next step in mastering future-ready skills. Visit Digital Regenesys.
What is DevOps? – FAQs
What exactly does DevOps mean?
DevOps is a combination of practices and tools that improve collaboration between development and operations teams while automating software delivery.
How is DevOps different from Agile?
Agile focuses on iterative development, while DevOps extends Agile principles into operations, ensuring smooth deployment and monitoring.
What industries use DevOps?
DevOps is utilised across various industries, including IT, finance, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing, to enhance digital transformation and drive innovation.
Is DevOps only about tools?
No. While tools are important, the essence of DevOps lies in culture, collaboration, and shared accountability.
How does DevOps improve security?
With DevSecOps, security is integrated into each stage of development, ensuring compliance and minimising risks.
Is DevOps a good career choice?
Yes. With rising adoption, DevOps engineers and specialists are among the most in-demand roles globally.

Leave a Reply